CILICIA
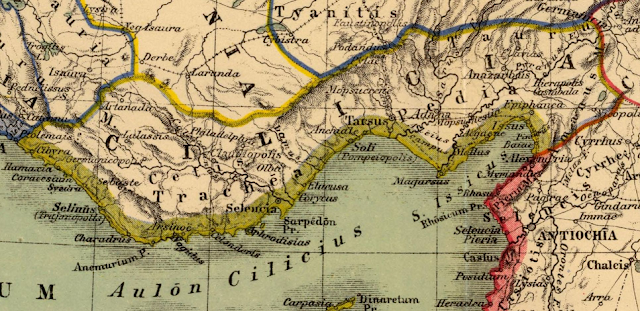 Neolithic to Neo-Assyrian period Cilicia was settled from the Neolithic period onwards.[27][28][page needed] Dating of the ancient settlements of the region from Neolithic to Bronze Age is as follows: Aceramic/Neolithic: 8th and 7th millennia BC; Early Chalcolithic: 5800 BC; Middle Chalcolithic (correlated with Halaf and Ubaid developments in the east): c. 5400–4500 BC; Late Chalcolithic: 4500–c. 3400 BC; and Early Bronze Age IA: 3400–3000 BC; EBA IB: 3000–2700 BC; EBA II: 2700–2400 BC; EBA III A-B: 2400–2000 BC.[28]: 168–170 Probable captives from Cilicia, on the Nasiriyah stele of Naram-Sin, circa 2200 BC.[29]The area had been known as Kizzuwatna in the earlier Hittite era (2nd millennium BC).[30][31] The region was divided into two parts, Uru Adaniya (flat Cilicia), a well-watered plain, and "rough" Cilicia (Tarza), in the mountainous west.
Neolithic to Neo-Assyrian period Cilicia was settled from the Neolithic period onwards.[27][28][page needed] Dating of the ancient settlements of the region from Neolithic to Bronze Age is as follows: Aceramic/Neolithic: 8th and 7th millennia BC; Early Chalcolithic: 5800 BC; Middle Chalcolithic (correlated with Halaf and Ubaid developments in the east): c. 5400–4500 BC; Late Chalcolithic: 4500–c. 3400 BC; and Early Bronze Age IA: 3400–3000 BC; EBA IB: 3000–2700 BC; EBA II: 2700–2400 BC; EBA III A-B: 2400–2000 BC.[28]: 168–170 Probable captives from Cilicia, on the Nasiriyah stele of Naram-Sin, circa 2200 BC.[29]The area had been known as Kizzuwatna in the earlier Hittite era (2nd millennium BC).[30][31] The region was divided into two parts, Uru Adaniya (flat Cilicia), a well-watered plain, and "rough" Cilicia (Tarza), in the mountainous west.
BITHYNIA
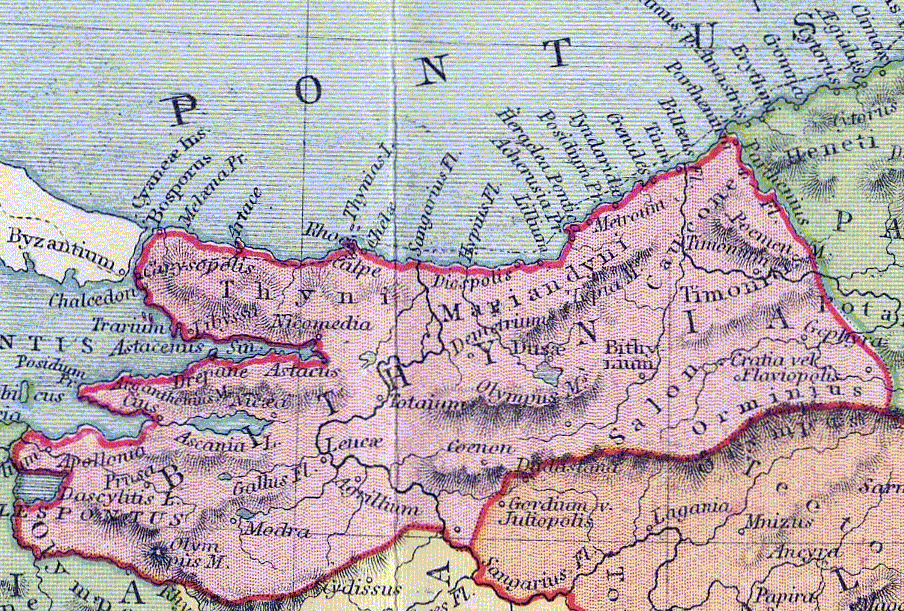 Bithynia (/bɪˈθɪniə/; Koine Greek: Βιθυνία, Bithynía) was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor, adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Paphlagonia to the northeast along the Pontic coast, and Phrygia to the southeast towards the interior of Asia Minor. Bithynia was an independent kingdom from the 4th century BC. Its capital Nicomedia was rebuilt on the site of ancient Astacus in 264 BC by Nicomedes I of Bithynia. Bithynia was bequeathed to the Roman Republic in 74 BC, and became united with the Pontus region as the province of Bithynia et Pontus. In the 7th century it was incorporated into the Byzantine Opsikion theme. It became a border region to the Seljuk Empire in the 13th century, and was eventually conquered by the Ottoman Turks between 1325 and 1333.
Bithynia (/bɪˈθɪniə/; Koine Greek: Βιθυνία, Bithynía) was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor, adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Paphlagonia to the northeast along the Pontic coast, and Phrygia to the southeast towards the interior of Asia Minor. Bithynia was an independent kingdom from the 4th century BC. Its capital Nicomedia was rebuilt on the site of ancient Astacus in 264 BC by Nicomedes I of Bithynia. Bithynia was bequeathed to the Roman Republic in 74 BC, and became united with the Pontus region as the province of Bithynia et Pontus. In the 7th century it was incorporated into the Byzantine Opsikion theme. It became a border region to the Seljuk Empire in the 13th century, and was eventually conquered by the Ottoman Turks between 1325 and 1333.
CARIA
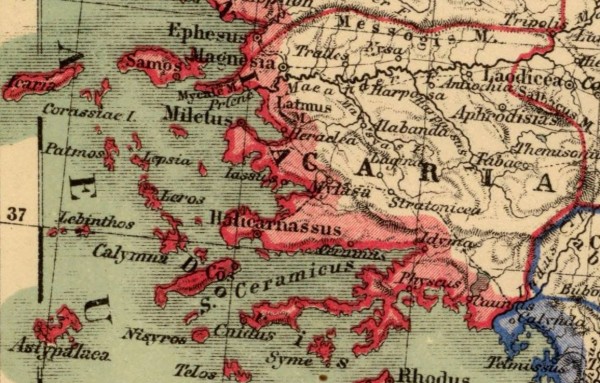 Caria (/ˈkɛəriə/; from Greek: Καρία, Karia, Turkish: Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia.[1] The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. The inhabitants of Caria, known as Carians, had arrived there before the Ionian and Dorian Greeks. They were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan descent,[2] while the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians.[2] The Carians did speak an Anatolian language, known as Carian, which does not necessarily reflect their geographic origin, as Anatolian once may have been widespread.[citation needed] Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians or for a people who had preceded them in the region and continued to exist as part of their society in a reputedly second-class status.
Caria (/ˈkɛəriə/; from Greek: Καρία, Karia, Turkish: Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia.[1] The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. The inhabitants of Caria, known as Carians, had arrived there before the Ionian and Dorian Greeks. They were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan descent,[2] while the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians.[2] The Carians did speak an Anatolian language, known as Carian, which does not necessarily reflect their geographic origin, as Anatolian once may have been widespread.[citation needed] Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians or for a people who had preceded them in the region and continued to exist as part of their society in a reputedly second-class status.
GALTIA
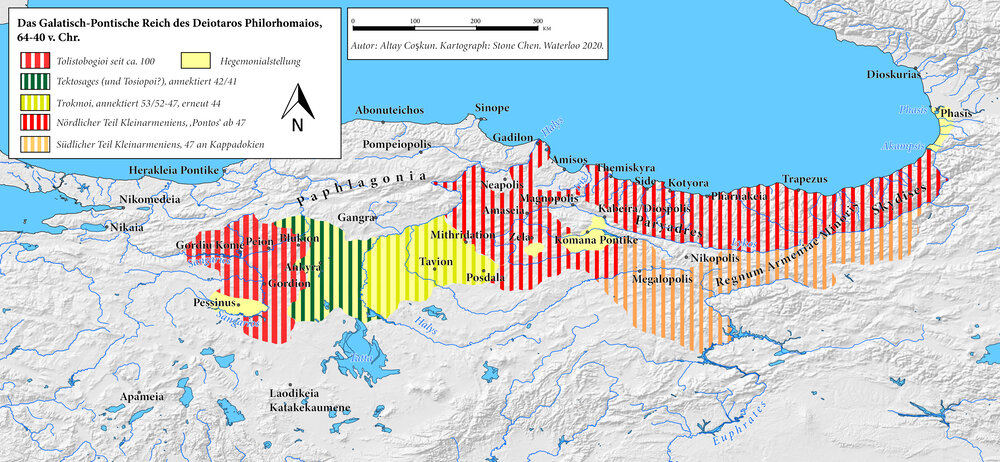 Galatia (/ɡəˈleɪʃə/; Ancient Greek: Γαλατία, Galatía, "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here and became a small transient foreign tribe in the 3rd century BC, following the supposed Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of the East; Roman writers calling its inhabitants Galli (Gauls or Celts).
Galatia (/ɡəˈleɪʃə/; Ancient Greek: Γαλατία, Galatía, "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (cf. Tylis), who settled here and became a small transient foreign tribe in the 3rd century BC, following the supposed Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of the East; Roman writers calling its inhabitants Galli (Gauls or Celts).
LYDIA
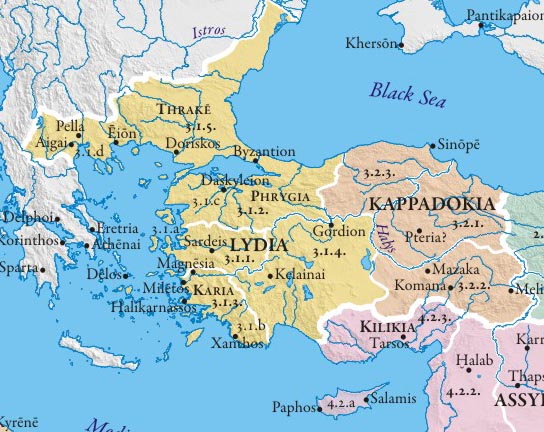 Lydia (Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, Śfarda; Aramaic: Lydia; Greek: Λυδία, Lȳdíā; Turkish: Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak, Manisa and inland İzmir. The language of its population, known as Lydian, was a member of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. Its capital was Sardis.
Lydia (Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, Śfarda; Aramaic: Lydia; Greek: Λυδία, Lȳdíā; Turkish: Lidya) was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak, Manisa and inland İzmir. The language of its population, known as Lydian, was a member of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. Its capital was Sardis.
The Kingdom of Lydia existed from about 1200 BC to 546 BC. At its greatest extent, during the 7th century BC, it covered all of western Anatolia. In 546 BC, it became a province of the Achaemenid Persian Empire, known as the satrapy of Lydia or Sparda in Old Persian. In 133 BC, it became part of the Roman province of Asia.
LYCIA
 Lycia (Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 Trm̃mis; Greek: Λυκία, Lykia; Turkish: Likya) was a geopolitical region in Anatolia in what are now the provinces of Antalya and Muğla on the southern coast of Turkey, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, and Burdur Province inland. Known to history since the records of ancient Egypt and the Hittite Empire in the Late Bronze Age, it was populated by speakers of the Luwian language group. Written records began to be inscribed in stone in the Lycian language (a later form of Luwian) after Lycia's involuntary incorporation into the Achaemenid Empire in the Iron Age. At that time (546 BC) the Luwian speakers were decimated, and Lycia received an influx of Persian speakers. Ancient sources seem to indicate that an older name of the region was Alope (Ancient Greek: Ἀλόπη, Alópē).
Lycia (Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 Trm̃mis; Greek: Λυκία, Lykia; Turkish: Likya) was a geopolitical region in Anatolia in what are now the provinces of Antalya and Muğla on the southern coast of Turkey, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, and Burdur Province inland. Known to history since the records of ancient Egypt and the Hittite Empire in the Late Bronze Age, it was populated by speakers of the Luwian language group. Written records began to be inscribed in stone in the Lycian language (a later form of Luwian) after Lycia's involuntary incorporation into the Achaemenid Empire in the Iron Age. At that time (546 BC) the Luwian speakers were decimated, and Lycia received an influx of Persian speakers. Ancient sources seem to indicate that an older name of the region was Alope (Ancient Greek: Ἀλόπη, Alópē).
LONIA
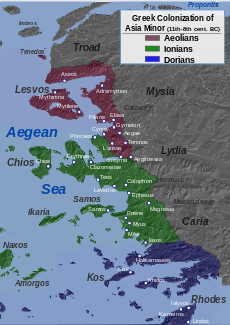 Ionia (/aɪˈoʊniə/; Ancient Greek: Ἰωνία /i.ɔː.ní.aː/, Iōnía or Ἰωνίη, Iōníē) was an ancient region on the central part of the western coast of Anatolia in present-day Turkey, the region nearest İzmir, which was historically Smyrna. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian tribe who, in the Archaic Period (600–480 BC), settled mainly the shores and islands of the Aegean Sea. Ionian states were identified by tradition and by their use of Eastern Greek.
Ionia (/aɪˈoʊniə/; Ancient Greek: Ἰωνία /i.ɔː.ní.aː/, Iōnía or Ἰωνίη, Iōníē) was an ancient region on the central part of the western coast of Anatolia in present-day Turkey, the region nearest İzmir, which was historically Smyrna. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian tribe who, in the Archaic Period (600–480 BC), settled mainly the shores and islands of the Aegean Sea. Ionian states were identified by tradition and by their use of Eastern Greek.
MYSIA
 Mysia (UK /ˈmɪsiə/, US /ˈmɪʒə/ or /ˈmiːʒə/; Greek: Μυσία, Latin: Mysia, Turkish: Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor[1] (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the east, Phrygia on the southeast, Lydia on the south, Aeolis on the southwest, Troad on the west and by the Propontis on the north. In ancient times it was inhabited by the Mysians, Phrygians, Aeolian Greeks and other groups.
Mysia (UK /ˈmɪsiə/, US /ˈmɪʒə/ or /ˈmiːʒə/; Greek: Μυσία, Latin: Mysia, Turkish: Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor[1] (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the east, Phrygia on the southeast, Lydia on the south, Aeolis on the southwest, Troad on the west and by the Propontis on the north. In ancient times it was inhabited by the Mysians, Phrygians, Aeolian Greeks and other groups.




